I want to create two buttons. Each should scroll sideways in a <$scrollable> container. They should scroll an X amount of pixels depending on the width of the container -10px. Is it possible to do this in a <$scrollable> container?
I am currently looking at $:/core/modules/widgets/scrollable.js.
I am specifically looking at this part of the code:
var getEndPos = function(targetPos,targetSize,currentPos,currentSize) {
// If the target is already visible then stay where we are
if(targetPos >= currentPos && (targetPos + targetSize) <= (currentPos + currentSize)) {
return currentPos;
// If the target is above/left of the current view, then scroll to its top/left
} else if(targetPos <= currentPos) {
return targetPos;
// If the target is smaller than the window and the scroll position is too far up, then scroll till the target is at the bottom of the window
} else if(targetSize < currentSize && currentPos < (targetPos + targetSize - currentSize)) {
return targetPos + targetSize - currentSize;
// If the target is big, then just scroll to the top
} else if(currentPos < targetPos) {
return targetPos;
// Otherwise, stay where we are
} else {
return currentPos;
}
},
This is making me wonder if I could create a new function or macro where I could use currentPos and subtract or add this.outerDomNode.offsetWidth depending on the button.
I was thinking of something like this:
return currentPos - this.outerDomNode.offsetWidth // to scroll left
return currentPos + this.outerDomNode.offsetWidth // to scroll right
I changed:
return currentPos - this.outerDomNode.offsetWidth // to scroll left
return currentPos + this.outerDomNode.offsetWidth // to scroll right
to:
return currentPos - currentSize // to scroll left
return currentPos + currentSize // to scroll right
I have tested this part of the code, and it worked on targetPos and currentPos. I just need to find a way to call currentPos and targetSize without the need of a CSS selector.
I suggest taking a step back and explaining your actual use case, ideally with an example.
I want a “scroll left” and “scroll right” buttons that would work inside a <$scrollable> container.
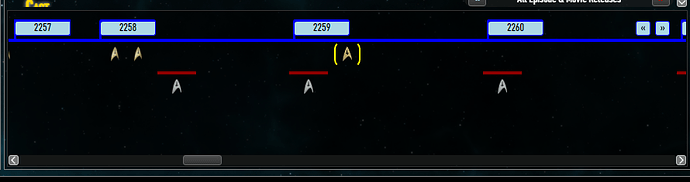
Below is a sample image of my project on TWC, which works just fine with JavaScript. In the upper-right corner are the buttons that I want:
This graphic shows the buttons. They scroll left and right depending on the size of the container:
If the container was 200px and you wanted to scroll left, it would go left 190px, and the same thing if you were to scroll right.
Here is a link to the JSFiddle file that does exactly what I want, but is programmed in JavaScript. I just don’t know how to do with TW5 and was hoping that tm-scroll would have a solution.
https://jsfiddle.net/RedAsset/pakx0cfo/8/
If you dont need animation you can do that with html anchor :
It’s also possible to use CSS to achieve a similar result with smooth transition :
I got this work as intended, but I had to hijack the code in $:/core/modules/widgets/scrollable.js to make this work like this:
/*\
title: $:/core/modules/widgets/scrollable.js
type: application/javascript
module-type: widget
Scrollable widget
\*/
(function(){
/*jslint node: true, browser: true */
/*global $tw: false */
"use strict";
var Widget = require("$:/core/modules/widgets/widget.js").widget;
This is where I needed to create a global variable so that, it can be accessed within the entire module. The “direction” variable is defined as “none” so that tm-scroll can be used for it’s original purpose:
+var direction = "none"; //later will be defined with "left" or "right" if needed.
var ScrollableWidget = function(parseTreeNode,options) {
this.initialise(parseTreeNode,options);
};
/*
Inherit from the base widget class
*/
ScrollableWidget.prototype = new Widget();
ScrollableWidget.prototype.cancelScroll = function() {
if(this.idRequestFrame) {
this.cancelAnimationFrame.call(window,this.idRequestFrame);
this.idRequestFrame = null;
}
};
/*
Handle a scroll event
*/
ScrollableWidget.prototype.handleScrollEvent = function(event) {
// Pass the scroll event through if our offsetsize is larger than our scrollsize
if(this.outerDomNode.scrollWidth <= this.outerDomNode.offsetWidth && this.outerDomNode.scrollHeight <= this.outerDomNode.offsetHeight && this.fallthrough === "yes") {
return true;
}
var options = {};
if($tw.utils.hop(event.paramObject,"animationDuration")) {
options.animationDuration = event.paramObject.animationDuration;
}
if(event.paramObject && event.paramObject.selector) {
I added an if statement here so I can define the “direction” variable:
+if (event.paramObject.selector == "#left" || event.paramObject.selector == "#right") {
+ direction = event.paramObject.selector;
+}
this.scrollSelectorIntoView(null,event.paramObject.selector,null,options);
} else {
this.scrollIntoView(event.target,null,options);
}
return false; // Handled event
};
/*
Scroll an element into view
*/
ScrollableWidget.prototype.scrollIntoView = function(element,callback,options) {
var duration = $tw.utils.hop(options,"animationDuration") ? parseInt(options.animationDuration) : $tw.utils.getAnimationDuration(),
srcWindow = element ? element.ownerDocument.defaultView : window;
this.cancelScroll();
this.startTime = Date.now();
var scrollPosition = {
x: this.outerDomNode.scrollLeft,
y: this.outerDomNode.scrollTop
};
// Get the client bounds of the element and adjust by the scroll position
var scrollableBounds = this.outerDomNode.getBoundingClientRect(),
clientTargetBounds = element.getBoundingClientRect(),
bounds = {
left: clientTargetBounds.left + scrollPosition.x - scrollableBounds.left,
top: clientTargetBounds.top + scrollPosition.y - scrollableBounds.top,
width: clientTargetBounds.width,
height: clientTargetBounds.height
};
// We'll consider the horizontal and vertical scroll directions separately via this function
var getEndPos = function(targetPos,targetSize,currentPos,currentSize) {
This is the part where I was looking at earlier. I added another if statement here. This will scroll left or right for the width of the container. Also everything was changed to “targetPos”:
+if (direction == "#left") {
+ return currentPos = currentPos - currentSize;
+}
+else if (direction == "#right") {
+ return currentPos = currentPos + currentSize;
+}
+else {
// If the target is already visible then stay where we are
if(targetPos >= currentPos && (targetPos + targetSize) <= (currentPos + currentSize)) {
return targetPos;
// If the target is above/left of the current view, then scroll to its top/left
} else if(targetPos <= currentPos) {
return targetPos;
// If the target is smaller than the window and the scroll position is too far up, then scroll till the target is at the bottom of the window
} else if(targetSize < currentSize && currentPos < (targetPos + targetSize - currentSize)) {
return targetPos + targetSize - currentSize;
// If the target is big, then just scroll to the top
} else if(currentPos < targetPos) {
return targetPos;
// Otherwise, stay where we are
} else {
return targetPos;
}
+}
},
endX = getEndPos(bounds.left,bounds.width,scrollPosition.x,this.outerDomNode.offsetWidth),
endY = getEndPos(bounds.top,bounds.height,scrollPosition.y,this.outerDomNode.offsetHeight);
// Only scroll if necessary
if(endX !== scrollPosition.x || endY !== scrollPosition.y) {
var self = this,
drawFrame;
drawFrame = function () {
/* last line code is added here */
Finally, I needed to reset “direction” back to “none”, otherwise tm-scroll would be could not be used for it’s original purpose:
+direction = "none";
var t;
if(duration <= 0) {
t = 1;
} else {
t = ((Date.now()) - self.startTime) / duration;
}
if(t >= 1) {
self.cancelScroll();
t = 1;
}
t = $tw.utils.slowInSlowOut(t);
self.outerDomNode.scrollLeft = scrollPosition.x + (endX - scrollPosition.x) * t;
self.outerDomNode.scrollTop = scrollPosition.y + (endY - scrollPosition.y) * t;
if(t < 1) {
self.idRequestFrame = self.requestAnimationFrame.call(srcWindow,drawFrame);
}
};
drawFrame();
}
};
ScrollableWidget.prototype.scrollSelectorIntoView = function(baseElement,selector,callback,options) {
baseElement = baseElement || document.body;
var element = baseElement.querySelector(selector);
if(element) {
this.scrollIntoView(element,callback,options);
}
};
/*
Render this widget into the DOM
*/
ScrollableWidget.prototype.render = function(parent,nextSibling) {
var self = this;
this.scaleFactor = 1;
this.addEventListeners([
{type: "tm-scroll", handler: "handleScrollEvent"}
]);
if($tw.browser) {
this.requestAnimationFrame = window.requestAnimationFrame ||
window.webkitRequestAnimationFrame ||
window.mozRequestAnimationFrame ||
function(callback) {
return window.setTimeout(callback, 1000/60);
};
this.cancelAnimationFrame = window.cancelAnimationFrame ||
window.webkitCancelAnimationFrame ||
window.webkitCancelRequestAnimationFrame ||
window.mozCancelAnimationFrame ||
window.mozCancelRequestAnimationFrame ||
function(id) {
window.clearTimeout(id);
};
}
// Remember parent
this.parentDomNode = parent;
// Compute attributes and execute state
this.computeAttributes();
this.execute();
// Create elements
this.outerDomNode = this.document.createElement("div");
$tw.utils.setStyle(this.outerDomNode,[
{webkitOverflowScrolling: "touch"}
]);
this.innerDomNode = this.document.createElement("div");
this.outerDomNode.appendChild(this.innerDomNode);
// Assign classes
this.outerDomNode.className = this["class"] || "";
// Insert element
parent.insertBefore(this.outerDomNode,nextSibling);
this.renderChildren(this.innerDomNode,null);
this.domNodes.push(this.outerDomNode);
};
/*
Compute the internal state of the widget
*/
ScrollableWidget.prototype.execute = function() {
// Get attributes
this.fallthrough = this.getAttribute("fallthrough","yes");
this["class"] = this.getAttribute("class");
// Make child widgets
this.makeChildWidgets();
};
/*
Selectively refreshes the widget if needed. Returns true if the widget or any of its children needed re-rendering
*/
ScrollableWidget.prototype.refresh = function(changedTiddlers) {
var changedAttributes = this.computeAttributes();
if(changedAttributes["class"]) {
this.refreshSelf();
return true;
}
return this.refreshChildren(changedTiddlers);
};
exports.scrollable = ScrollableWidget;
})();
Then the code I used in the tiddler with the <$scrollable> container, where I had to add two div tags with the ids “left” and “right”, otherwise the widget wouldn’t function if it had nothing to find. They are just there as a placeholder. Then I just needed to make sure the values of the two buttons needed were set to “#left” and “#right”:
<$scrollable id="tta-timeline" class="tta-timeline">
<div id="left"/>
<div id="right"/>
<div class="tta-timeline-controls">
<$button>
<$action-sendmessage $message="tm-scroll" $name="selector" $value="#left" animationDuration="1000"/>
Left
</$button>
<$button>
<$action-sendmessage $message="tm-scroll" $name="selector" $value={{{ [<storyTiddler>get[tiddler-id]addprefix[#]] }}} animationDuration="1000"/>
Return
</$button>
<$button>
<$action-sendmessage $message="tm-scroll" $name="selector" $value="#right" animationDuration="1000"/>
Right
</$button>
</div>
</$scrollable>
Now, I am wondering how I can position: fixed my buttons inside the <$scrollable> container.
Hi, @RedAsset
can I build a button to scroll-down one screen with the js ?
And can I build a shortkey to do this?
By the way what is the tta-timeline? This also sound very interesting to me.
Hi @JanJo since the OP we’ve extended the scrollable widget. I’ve expanded one of the examples in the <$scrollable> widget docs to add buttons to scroll up/down by a fixed amount. The update will be live in 5-10 minutes at the end of this tiddler: